【LetMeFly】778.水位上升的泳池中游泳:(贪心)优先队列(附C++/Python/Java/Go/Rust优先队列方法表) 力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/swim-in-rising-water/
在一个 n x n 的整数矩阵 grid 中,每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示位置 (i, j) 的平台高度。
当开始下雨时,在时间为 t 时,水池中的水位为 t 。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发。返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台 (n-1, n-1) 所需的最少时间 。
示例 1:
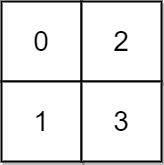
输入: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为 (0, 0)。
此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。
等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置
示例 2:
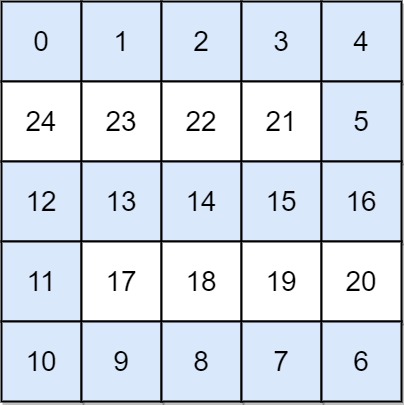
输入: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]]
输出: 16
解释: 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。
我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2 grid[i][j] 中每个值 均无重复
解题方法:贪心(优先队列) 解题思路
由于你可以在水中瞬移,所以你可以随意地进行尝试,并在发现更优解时瞬移过去继续。
想要找从左上角到右下角最大值尽可能小的一条路,可以使用一个优先队列,把所有的可以走但是还没走到的位置放入优先队列中,然后每次从中取出一个最小的值作为下一步。
具体方法 使用一个布尔类型的数组判断每个位置是否已经走过(贪心策略保证早走一定优于晚走)。使用一个优先队列放入所有可以走到的位置,初始值只有左上角的(0, 0)在优先队列中。
不断从优先队列中取出元素,从当前位置向上下左右四个方向进行尝试,并把没有走过的位置放入优先队列中。入队时更新整条路径中的最高点为当前点和上一个点的最大值。
特别的,一旦右下角的点可走,不用入队再出队了,函数直接返回就好。
思路解析 由于你可以瞬移,所以尝试是不值钱的。哪怕绕18圈也要让一路上的最高点尽可能低。
所以我们采用贪心策略,每次都在下一个能走到的位置中,选一个最低点走过去。
这样走到右下角时,路径的最高点一定是(可能绕来绕去)最低的。
时空复杂度分析
时间复杂度$O(n^2\log n)$
空间复杂度$O(n^2)$
C++/Python/Java/Go/Rust优先队列方法表
语言
数据结构
小顶堆 / 大顶堆
示例代码
说明
C++
priority_queue小顶堆(自定义 comparator)
auto cmp = [&grid](pair<int,int>& a, pair<int,int>& b) {使用 lambda 自定义比较函数,小的值优先。
Python
heapq小顶堆(默认)
import heapq用元组的第一个元素作为优先级,heapq 默认最小堆。
Go
container/heap小顶堆(自定义 Less)
import "container/heap"需要自定义类型和接口方法 Len/Swap/Less/Push/Pop。
Java
PriorityQueue小顶堆(自定义 Comparator)
import java.util.PriorityQueue;用数组存坐标对,Comparator 按 grid 值升序。
Rust
BinaryHeap + Reverse小顶堆(默认最大堆,需要 Reverse)
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;BinaryHeap 默认最大堆,使用 Reverse 包装最小值优先。
AC代码 下面代码实现中,可以处理给定grid不是正方形而是普通长方形的情况。
C++ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {private :static constexpr int direction[4 ][2 ] = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }};public :int swimInWater (vector<vector<int >>& grid) int n = grid.size (), m = grid[0 ].size ();if (n == 1 && m == 1 ) {return grid[0 ][0 ]; auto cmp = [&grid](pair<int , int >& a, pair<int , int >& b) {return grid[a.first][a.second] > grid[b.first][b.second]; int , int >, vector<pair<int , int >>, decltype (cmp)> pq (cmp);bool >> visited (n, vector <bool >(m));push ({0 , 0 });0 ][0 ] = true ;while (true ) {auto [x, y] = pq.top ();pop ();for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; d++) {int nx = x + direction[d][0 ], ny = y + direction[d][1 ];if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || visited[nx][ny]) {continue ;max (grid[nx][ny], grid[x][y]);if (nx == n - 1 && ny == m - 1 ) {return grid[nx][ny];true ;push ({nx, ny});
Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 ''' Author: LetMeFly Date: 2025-10-06 12:17:42 LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz LastEditTime: 2025-10-06 13:06:15 ''' from typing import List import heapqclass Solution :0 , 1 ], [0 , -1 ], [-1 , 0 ], [1 , 0 ]]def swimInWater (self, grid: List [List [int ]] ) -> int :len (grid), len (grid[0 ])if n == 1 and m == 1 :return grid[0 ][0 ]False ] * m for _ in range (n)]0 ][0 ], 0 , 0 )]0 ][0 ] = True while True :for dx, dy in self .directions:if (not (0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m)) or visited[nx][ny]:continue max (grid[nx][ny], val)if nx == n - 1 and ny == m - 1 :return grid[nx][ny]True
Java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import java.util.PriorityQueue;class Solution {private static final int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {-1 , 0 }};public int swimInWater (int [][] grid) {int n = grid.length, m = grid[0 ].length;if (n == 1 && m == 1 ) {return grid[0 ][0 ];boolean [][] visited = new boolean [n][m];int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <>((a, b) -> grid[a[0 ]][a[1 ]] - grid[b[0 ]][b[1 ]]);new int []{0 , 0 });0 ][0 ] = true ;while (true ) {int [] top = pq.poll();int x = top[0 ], y = top[1 ];for (int [] d : directions) {int nx = x + d[0 ], ny = y + d[1 ];if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || visited[nx][ny]) {continue ;if (nx == n - 1 && ny == m - 1 ) {return grid[nx][ny];true ;new int []{nx, ny});
Go 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 package mainimport "container/heap" type Item778 struct {int int type PriorityQueue778 []*Item778var directions778 = [][]int {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }}func swimInWater (grid [][]int ) int {len (grid), len (grid[0 ])if n == 1 && m == 1 {return grid[0 ][0 ]make ([][]bool , n)for i, _ := range visited {make ([]bool , m)0 , 0 , grid[0 ][0 ]})0 ][0 ] = true for true {for _, d := range directions778 {0 ], y + d[1 ]if nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || visited[nx][ny] {continue if nx == n - 1 && ny == m - 1 {return grid[nx][ny]true return -1 func (pq PriorityQueue778) int { return len (pq) }func (pq PriorityQueue778) int ) bool { return pq[i].val < pq[j].val }func (pq PriorityQueue778) int ) { pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i] }func (pq *PriorityQueue778) append (*pq, x.(*Item778)) }func (pq *PriorityQueue778) len (*pq); item := (*pq)[n - 1 ]; *pq = (*pq)[:n-1 ]; return item }
Rust 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 use std::collections::BinaryHeap;use std::cmp::Reverse;impl Solution {const DIRECTIONS: [[i32 ; 2 ]; 4 ] = [[0 , 1 ], [0 , -1 ], [-1 , 0 ], [1 , 0 ]];pub fn swim_in_water (grid: Vec <Vec <i32 >>) -> i32 {let n : usize = grid.len ();let m : usize = grid[0 ].len ();if n == 1 && m == 1 {return grid[0 ][0 ];let mut pq = BinaryHeap::new ();let mut visited : Vec <Vec <bool >> = vec! [vec! [false ; m]; n];push (Reverse ((grid[0 ][0 ], 0 , 0 )));0 ][0 ] = true ;while let Some (Reverse ((val, x, y))) = pq.pop () {for &[dx, dy] in Self ::DIRECTIONS.iter () {let nx : usize = x + dx as usize ; let ny : usize = y + dy as usize ; if nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || visited[nx][ny] {continue ;let n_val : i32 = val.max (grid[nx][ny]);if nx == n - 1 && ny == m - 1 {return n_val;true ;push (Reverse ((n_val, nx, ny)));1
同步发文于CSDN 和我的个人博客 ,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接 哦~
千篇源码题解已开源