【LetMeFly】3249.统计好节点的数目:深度优先搜索(DFS)
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-good-nodes/
现有一棵 无向 树,树中包含 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n - 1 标记。树的根节点是节点 0 。给你一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 与节点 bi 之间存在一条边。
如果一个节点的所有子节点为根的 子树 包含的节点数相同,则认为该节点是一个 好节点。
返回给定树中 好节点 的数量。
子树 指的是一个节点以及它所有后代节点构成的一棵树。
示例 1:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
输出:7
说明:
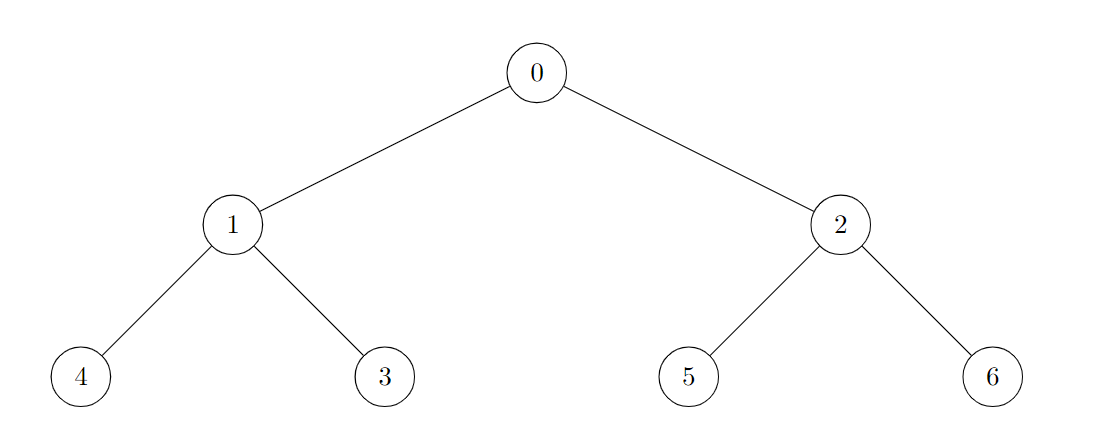
树的所有节点都是好节点。
示例 2:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,5],[1,6],[2,7],[3,8]]
输出:6
说明:
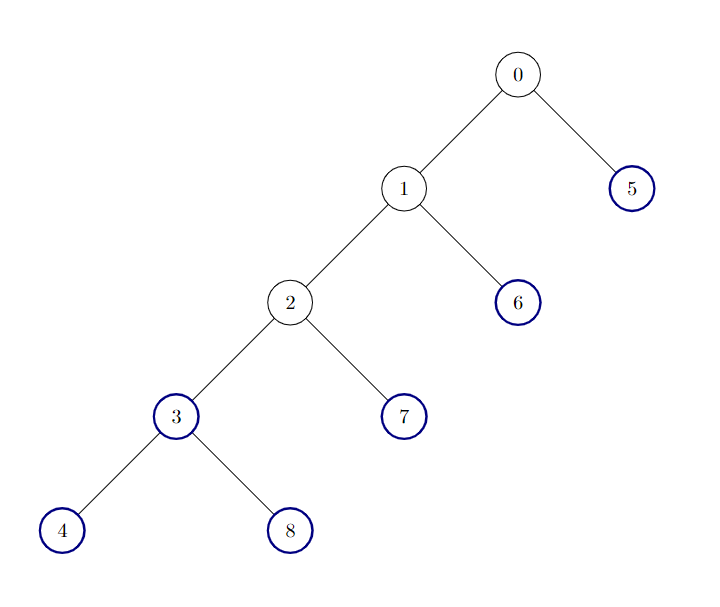
树中有 6 个好节点。上图中已将这些节点着色。
示例 3:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],[0,9],[9,10],[9,12],[10,11]]
输出:12
解释:
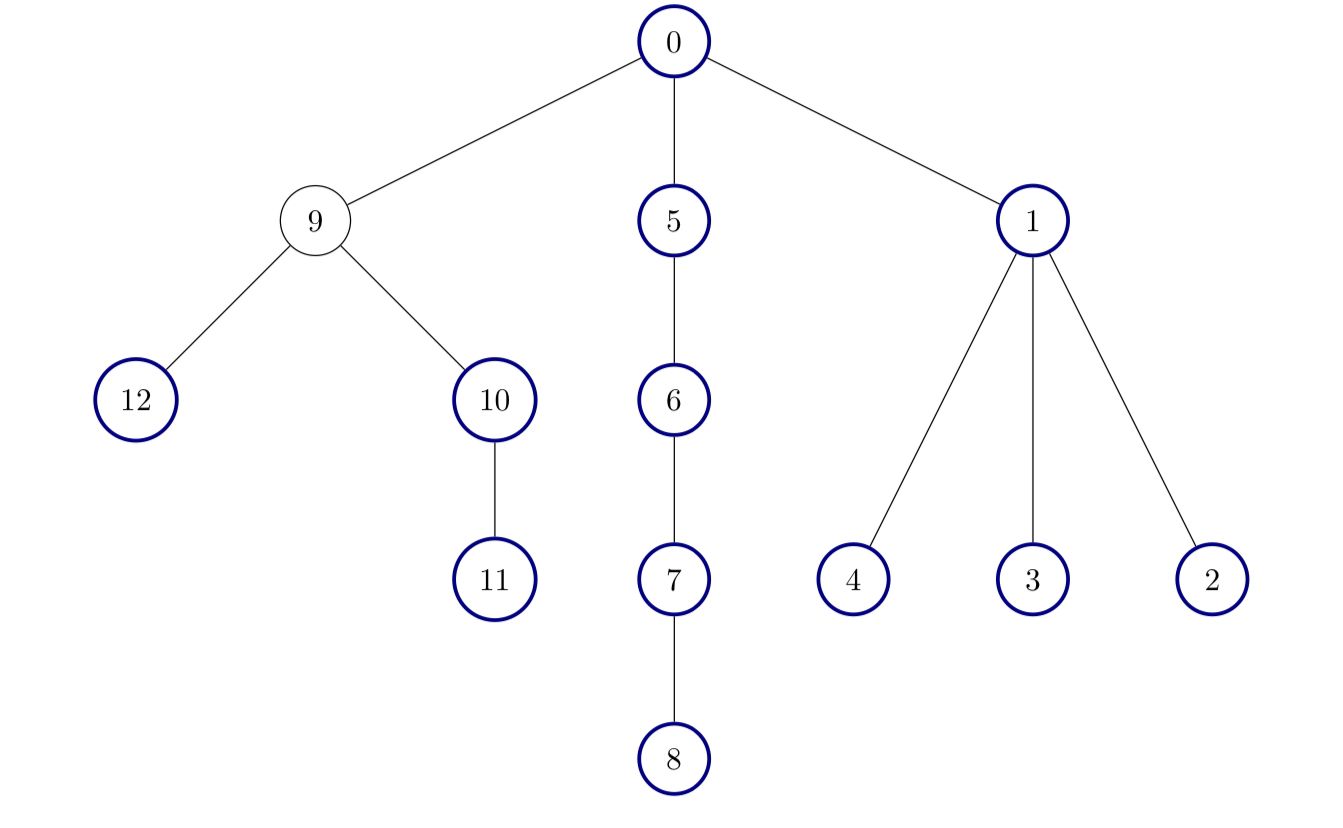
除了节点 9 以外其他所有节点都是好节点。
提示:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < n- 输入确保
edges 总表示一棵有效的树。
解题方法:深度优先搜索
首先通过“边”建“树”,创建一个graph二维数组,其中graph[x]为所有与x相邻的节点。
接着写一个函数dfs(当前节点, 父节点),如果当前节点的所有子树大小dfs(子节点)相同,就将全局答案加一。最终返回当前节点为根的子树的大小。
- 时间复杂度$O(n)$,每个节点之后被
dfs一次
- 空间复杂度$O(n)$
AC代码
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| class Solution {
private:
int ans;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
int dfs(int root, int parent=-1) {
int cnt = 1;
int oneChild = 0;
bool thisNodeOk = true;
for (int nextNode : graph[root]) {
if (nextNode == parent) {
continue;
}
int nextCnt = dfs(nextNode, root);
cnt += nextCnt;
if (oneChild && nextCnt != oneChild) {
thisNodeOk = false;
}
oneChild = nextCnt;
}
if (thisNodeOk) {
ans++;
}
return cnt;
}
public:
int countGoodNodes(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
ans = 0;
graph.resize(edges.size() + 1);
for (vector<int>& edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);
}
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
|
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| from typing import List
class Solution:
def dfs(self, thisNode: int, parentNode: int=-1) -> int:
cnt, oneChild, ok = 1, 0, True
for nextNode in self.graph[thisNode]:
if nextNode == parentNode:
continue
nextChild = self.dfs(nextNode, thisNode)
cnt += nextChild
if not oneChild:
oneChild = nextChild
elif oneChild != nextChild:
ok = False
if ok:
self.ans += 1
return cnt
def countGoodNodes(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
self.graph = [[] for _ in range(len(edges) + 1)]
for x, y in edges:
self.graph[x].append(y)
self.graph[y].append(x)
self.ans = 0
self.dfs(0)
return self.ans
|
Java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] graph;
private int ans;
private int dfs(int thisNode, int lastNode) {
int cnt = 1;
int oneChild = 0;
boolean ok = true;
for (int nextChilld : graph[thisNode]) {
if (nextChilld == lastNode) {
continue;
}
int thisChild = dfs(nextChilld, thisNode);
cnt += thisChild;
if (oneChild == 0) {
oneChild = thisChild;
} else if (oneChild != thisChild) {
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
ans++;
}
return cnt;
}
public int countGoodNodes(int[][] edges) {
ans = 0;
graph = new ArrayList[edges.length + 1];
Arrays.setAll(graph, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
}
|
Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package main
func countGoodNodes(edges [][]int) (ans int) {
graph := make([][]int, len(edges) + 1)
for _, edge := range edges {
graph[edge[0]] = append(graph[edge[0]], edge[1])
graph[edge[1]] = append(graph[edge[1]], edge[0])
}
var dfs func(int, int) int
dfs = func(thisNode, lastNode int) int {
cnt, oneChild, ok := 1, 0, true
for _, nextNode := range graph[thisNode] {
if nextNode == lastNode {
continue
}
thisChild := dfs(nextNode, thisNode)
cnt += thisChild
if oneChild == 0 {
oneChild = thisChild
} else if oneChild != thisChild {
ok = false
}
}
if ok {
ans++
}
return cnt
}
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
}
|
同步发文于CSDN和我的个人博客,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/143768804
BTW: 力扣昨天(2024.11.14)上午可以显示在线人员数量了(正在做这道题的人数)


