【LetMeFly】685.冗余连接 II:并查集(和I有何不同分析)——详细题解(附图) 力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/redundant-connection-ii/
在本问题中,有根树指满足以下条件的 有向 图。该树只有一个根节点,所有其他节点都是该根节点的后继。该树除了根节点之外的每一个节点都有且只有一个父节点,而根节点没有父节点。
输入一个有向图,该图由一个有着 n 个节点(节点值不重复,从 1 到 n)的树及一条附加的有向边构成。附加的边包含在 1 到 n 中的两个不同顶点间,这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。
结果图是一个以边组成的二维数组 edges 。 每个元素是一对 [ui , vi ],用以表示 有向 图中连接顶点 ui 和顶点 vi 的边,其中 ui 是 vi 的一个父节点。
返回一条能删除的边,使得剩下的图是有 n 个节点的有根树。若有多个答案,返回最后出现在给定二维数组的答案。
示例 1:
输入: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
输出: [2,3]
示例 2:
输入: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,1],[1,5]]
输出: [4,1]
提示:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ui , vi <= n
解题方法:并查集
解题思路 这题和684.冗余连接 的区别是:
684的无向图只需要考虑有没有形成自环,而本题有向图还需要考虑“是否形成了入度为2的节点”。
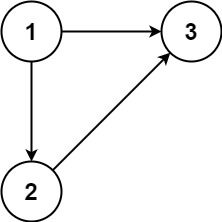
如果形成了“入度为2”的节点,例如下面两种情况,在684.冗余连接中只需要移除“首次形成(无向)环”的边,而在685.冗余连接II中就不能只移除“最后出现的导致形成(无向)环的边”:
1 2 3 ----- >------+ ------+ <----- <---
左图中只能移除[1,2]或[3,2]而不能移除[3,1];右图中只能移除[1,3]而不能移除[3,2]或[2,1]。
有向边不能和无向边一概而论的本质原因是:树中一个节点不能有两个父节点,即入度不能为2。所以,一旦出现了入度为2的节点$node$,就要在“终点为$node$的两条边”里面选择一条移除。判断方法如下:
尝试移除一条边,判断剩下的边(不考虑方向)能否构成无向环,如果不构成无向环则说明这条边可以被移除。
判断方法就和684题一模一样了,使用并查集即可完成判断。
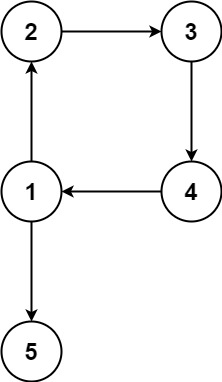
树上多一条边就一定存在入度为2的节点吗?不一定,还可能有以下这种情况:
图中节点[1,2,3]形成了一个环,但1、2、3、44个节点的入度都为1。
这样就和684题一模一样了其实,在环[1,2,3]里任意移除一条边图都能变成树。
同样使用并查集,返回第一条“形成环”的边即为所求。
解题方法 首先统计是否有入度为2的节点:
若有,则尝试移除指向2的边(若移除后图中无环则这条边可以被移除)
否则,移除第一条导致“环出现”的边
常见问题回答Q&A Q1: 若有入度为2的节点,在判断“移除一条边后图是否为树”时,能否通过“统计每个点是否孤立(入度出度都为0)”来判断?
例如下图中终点为3的边有[1,3]和[4,3]两条,移除[4,3]的话会导致点4成为孤立点,因此只能移除[1,3]。
A1: 不能这么判断。例如下图只能移除[2,4]不能移除[5,2],但其实移除其中的任意一条都不会产生“孤立点”。
1 2 3 4 5 +---+4 -->2 1 -->5 -->3
建议修改为“通过判断图是否联通”的方式判断某条边是否可以移除。
时空复杂度
时间复杂度最坏$O(n\log n)$,平均为$O(n\alpha(n))$(接近$O(n)$)
空间复杂度$O(n)$
AC代码 C++ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 class Solution {private :int > fa;bool couldRemoveThisEdge (vector<vector<int >>& edges, int index) initFa (edges.size ());for (int i = 0 ; i < edges.size (); i++) {if (i == index) {continue ;if (find (edges[i][0 ]) == find (edges[i][1 ])) {return false ;union_ (edges[i][0 ], edges[i][1 ]);return true ;vector<int > solution_indegree (vector<vector<int >>& edges, int node) {for (int i = edges.size () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {if (edges[i][1 ] == node && couldRemoveThisEdge (edges, i)) {return edges[i];return {}; int find (int x) if (x != fa[x]) {find (fa[x]);return fa[x];void union_ (int x, int y) find (x)] = find (y);void initFa (int n) resize (n + 1 );for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {vector<int > solution_unionFind (vector<vector<int >>& edges) {initFa (edges.size ());for (vector<int >& edge : edges) {if (find (edge[0 ]) == find (edge[1 ])) {return edge;else {union_ (edge[0 ], edge[1 ]);return {}; public :vector<int > findRedundantDirectedConnection (vector<vector<int >>& edges) {vector<bool > inDegree (edges.size() + 1 ) ;for (vector<int >& edge : edges) {if (inDegree[edge[1 ]]) { return solution_indegree (edges, edge[1 ]);else {1 ]] = true ;return solution_unionFind (edges);
Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 from typing import List class Solution :def initFa (self ) -> None :for i in range (1 , len (self .edges) + 1 ):self .fa[i] = idef find (self, x: int ) -> int :if self .fa[x] != x:self .fa[x] = self .find(self .fa[x])return self .fa[x]def union (self, x: int , y: int ) -> None :self .fa[self .find(x)] = self .find(y)def couldRemoveThisEdge (self, index: int ) -> bool :self .initFa()for i in range (len (self .edges)):if i == index:continue if self .find(self .edges[i][0 ]) == self .find(self .edges[i][1 ]):return False else :self .union(self .edges[i][0 ], self .edges[i][1 ])return True def solution_indegree (self, node: int ) -> List [int ]:for i in range (len (self .edges) - 1 , -1 , -1 ):if self .edges[i][1 ] == node and self .couldRemoveThisEdge(i):return self .edges[i]return [] def solution_unionFind (self ) -> List [int ]:self .initFa()for x, y in self .edges:if self .find(x) == self .find(y):return [x, y]else :self .union(x, y)return [] def findRedundantDirectedConnection (self, edges: List [List [int ]] ) -> List [int ]:self .fa = [0 ] * (len (edges) + 1 )self .edges = edgesFalse ] * (len (edges) + 1 )for x, y in edges:if hasIndegree[y]:return self .solution_indegree(y)else :True return self .solution_unionFind()
Java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class UnionFind {private int [] fa;public UnionFind (int n) {new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {private int find (int x) {if (fa[x] != x) {return fa[x];public boolean isUnion (int x, int y) {return find(x) == find(y);public void union (int x, int y) {class Solution {private boolean canRemoveThisEdge (int [][] edges, int index) {UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind (edges.length);for (int i = 0 ; i < edges.length; i++) {if (i == index) {continue ;if (unionFind.isUnion(edges[i][0 ], edges[i][1 ])) {return false ;else {0 ], edges[i][1 ]);return true ;private int [] solution_indegree(int [][] edges, int node) {for (int i = edges.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {if (edges[i][1 ] == node && canRemoveThisEdge(edges, i)) {return edges[i];return new int [0 ]; private int [] solution_unionFind(int [][] edges) {UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind (edges.length);for (int [] edge : edges) {if (unionFind.isUnion(edge[0 ], edge[1 ])) {return edge;else {0 ], edge[1 ]);return new int [0 ]; public int [] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int [][] edges) {boolean [] hasIndegree = new boolean [edges.length + 1 ];for (int [] edge : edges) {if (hasIndegree[edge[1 ]]) {return solution_indegree(edges, edge[1 ]);else {1 ]] = true ;return solution_unionFind(edges);
Go 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 package maintype UnionFind struct {int func New (n int ) make ([]int , n + 1 )for th, _ := range fa {return UnionFind{fa}func (unionFind UnionFind) int ) int {if unionFind.fa[x] != x {return unionFind.fa[x]func (unionFind UnionFind) int ) bool {return unionFind._find(x) == unionFind._find(y)func (unionFind UnionFind) int ) {func canRemoveThisEdge (edges [][]int , index int ) bool {len (edges))for i := 0 ; i < len (edges); i++ {if i == index {continue if unionFind.isUnion(edges[i][0 ], edges[i][1 ]) {return false else {0 ], edges[i][1 ])return true func solution_indegree (edges [][]int , node int ) int {for i := len (edges) - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- {if edges[i][1 ] == node && canRemoveThisEdge(edges, i) {return edges[i]return make ([]int , 0 ) func solution_unionFind (edges [][]int ) int {len (edges))for _, edge := range edges {if unionFind.isUnion(edge[0 ], edge[1 ]) {return edgeelse {0 ], edge[1 ])return make ([]int , 0 ) func findRedundantDirectedConnection (edges [][]int ) int {make ([]bool , len (edges) + 1 )for _, edge := range edges {if hasIndegree[edge[1 ]] {return solution_indegree(edges, edge[1 ])else {1 ]] = true return solution_unionFind(edges)
同步发文于CSDN和我的个人博客 ,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接 哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/143470538